
Choosing the right fridge defrost heater can make a big difference in how your refrigerator works. Electric defrost heaters usually offer simple operation and quick results, making them a popular choice for homes. Hot gas systems often save more energy and work well in busy commercial kitchens. Some users like electric models for their easy maintenance, while others prefer hot gas for lower running costs. When picking a refrigerator defrost heater, think about your space and how often you need to use the defrost heater in freezer units. Many people also check the design of defrost heating pipes to see what fits best.
Key Takeaways
- Electric defrost heaters are easy to use, affordable, and best for home refrigerators with simple maintenance needs.
- Hot gas defrost heaters save more energy, keep temperatures steady, and work well in large commercial fridges.
- Smart controls and optimized heater designs can improve efficiency and reduce energy use for both heater types.
- Electric heaters may cause temperature swings and higher energy use, while hot gas systems need more complex installation and upkeep.
- Choose electric heaters for small spaces and hot gas systems for busy, large-scale refrigeration to balance cost and performance.
Fridge Defrost Heater Types Overview

Electric Defrost Heater Function
Electric defrost heaters use electrical energy to melt frost that builds up on the freezer’s evaporator coils. These heaters come in different forms, such as calrod, ceramic plate, and distributed heaters. Each type has its own way of spreading heat. For example, calrod heaters transfer heat by both radiation and convection, while ceramic plate heaters keep the freezer temperature rise lower, which means better efficiency.
Here’s a quick look at how different electric heater types perform:
| Heater Type | Power Rating (W) | Defrost Duration (min) | Energy Consumption (W·h) | Freezer Temperature Rise (K) | Defrost Efficiency / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calrod Heater | 200 | ~8.5 | ~118.8 | 5 to 12.6 | Efficient and low cost; heat by radiation and convection; lower efficiency than ceramic |
| Ceramic Plate Heater | N/A | N/A | N/A | Lower than calrod | Higher defrost efficiency; less temperature rise |
| Distributed Heater | 235 | 8.5 (uniform), 3.67 (aligned) | N/A | N/A | Faster defrost when matched to frost; heat density varies |
| Combined Conductive-Radiative | N/A | Reduced by optimization | N/A | Reduced from 11 K to 5 K | Pulsating power improves efficiency by up to 15% |
| Step-Reduction Power Control | N/A | Similar to constant | 27.1% energy reduction | Similar to constant | Reduces energy use without longer defrost |
| Hybrid with Frost Detection | 12 | N/A | 10% energy conservation | N/A | Uses frost thickness to save energy |
Electric heaters can use a constant power level, like 200 watts, or combine local and global heaters for better results. Distributed electric heaters improve defrosting by making sure heat reaches all frosted areas. This method can cut energy use by over 27% and shorten defrost time by up to 15 minutes. Electric heaters work well in small fridges and do not need big changes to the system.
Tip: Electric defrost heaters help keep freezer temperatures steady and prevent local overheating. This makes them a good choice for homes and small businesses.
Hot Gas Defrost Heater Function
Hot gas defrost heaters use the heat from the fridge’s own refrigerant gas to melt frost. Instead of using electricity, the system redirects hot gas through the evaporator coils. This method keeps the fridge running and reduces temperature swings inside.
Studies show that hot gas defrosting can boost heating capacity by over 10% and improve energy efficiency by about 4%. The temperature inside the fridge stays more stable, with less fluctuation compared to electric defrosting. Hot gas systems also keep the outlet air temperature steady, which helps protect stored food.
| Performance Metric | Hot Gas Bypass Defrosting Result | Comparison to Conventional Defrosting |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Capacity Increase | 10.17% higher | N/A |
| Energy Efficiency Improvement | 4.06% higher | N/A |
| Indoor Air Temperature Fluctuation Range | 1°C to 1.6°C | About 84% less than conventional defrosting |
| Outlet Air Temperature Decrease | Decreased by about 7°C | Fluctuation range 56% less than conventional |
| Maximum Outlet Temperature Stability | Stable at 35.2°C | N/A |
Hot gas defrost heaters work best in large or commercial fridges that run all day. They keep the system reliable and reduce the risk of big temperature drops during defrost cycles.
Electric Fridge Defrost Heater
Pros of Electric Fridge Defrost Heater
Electric defrost heaters have become a popular choice for many households and small businesses. People like them because they are easy to use and install. Most refrigerators with electric defrost systems work automatically, so users do not need to worry about turning them on or off. This convenience saves time and effort.
- Automatic Operation: Electric defrost heaters turn on and off by themselves. The system senses when frost builds up and starts the defrost cycle. This feature keeps the freezer running smoothly and helps maintain food quality.
- Reliable Performance: These heaters remove frost quickly and keep the evaporator coils clean. When frost builds up, it can block airflow and make the fridge work harder. Electric heaters solve this problem by melting the frost before it becomes an issue.
- Simple Maintenance: Most electric defrost systems do not need much attention. Users only need to clean the coils once in a while to keep the system working well. Regular cleaning can even lower energy use.
- Flexible Design: Manufacturers can use different types of electric heaters, such as calrod or ceramic plate, to match the needs of each fridge. This flexibility allows for better performance and energy savings.
Recent studies show that electric defrost heaters help keep refrigerators efficient. For example, field data from 195 refrigerators in Australia showed that these systems use between 0.2 to 0.5 Wh per day per liter. The defrost intervals ranged from 13 to 37 hours, which means the system does not run too often. Automatic defrosting also reduces the need for users to scrape off frost by hand.
Some new designs use smart control strategies to save even more energy. By optimizing when the heater turns on, engineers have improved defrosting efficiency by up to 6.7%. These improvements help lower electricity bills and keep food safe.
Cons of Electric Fridge Defrost Heater
While electric defrost heaters offer many benefits, they also have some drawbacks. One of the main concerns is energy use. Every time the heater runs, it adds to the fridge’s total power consumption. This can lead to higher electricity bills, especially if the defrost cycle happens too often.
- Increased Energy Consumption: Defrost cycles use extra power. For example, a 26 cu ft Kenmore fridge can use about 453 kWh per year, partly because of the defrost heater. Users may notice power spikes when the heater turns on.
- Temperature Fluctuations: When the heater melts frost, the temperature inside the freezer can rise quickly. Some tests show that the temperature can go up by about 1°C per minute during defrosting. This can affect how well the fridge keeps food cold.
- Control Challenges: The timing of defrost cycles depends on the control system. If the system is not set up well, it may run the heater more often than needed. This wastes energy and can shorten the life of the fridge.
- Real-World vs. Lab Performance: Laboratory tests often show lower energy use than what happens in real homes. In fact, lab tests can underestimate defrost energy by about 20%. This means users might see higher energy bills than expected.
Experts recommend cleaning the coils and checking the control settings to get the best performance. Some studies found that better condenser design and regular maintenance can cut energy use by over 30%.
Electric defrost heaters work best when users pay attention to maintenance and choose models with smart controls. By doing so, they can enjoy the benefits while keeping costs and energy use in check.
Hot Gas Fridge Defrost Heater

Pros of Hot Gas Fridge Defrost Heater
Hot gas defrost heaters bring several strong benefits, especially for large or commercial refrigerators. Many people choose this system because it uses the heat from the fridge’s own refrigerant gas. This method saves energy and keeps the fridge running smoothly.
- Energy Efficiency: Hot gas defrosting uses waste heat from the refrigeration cycle. This means the system does not need extra electricity for defrosting. Many businesses see lower energy bills with this setup.
- Stable Temperatures: The hot gas method keeps the inside temperature steady. Food stays safe because the temperature does not swing up and down as much during defrost cycles.
- Faster Defrost Cycles: Hot gas can melt frost quickly. This helps the fridge return to normal operation faster. Restaurants and grocery stores like this feature because it protects food quality.
- Less Wear on Components: The system does not rely on electric heating elements. This can mean fewer parts to replace and less risk of heater failure.
Note: Hot gas defrost heaters often work best in places where the fridge runs all day, like supermarkets or food warehouses. These environments need reliable and efficient defrosting.
Here’s a quick table showing some of the main advantages:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Savings | Uses existing heat, lowers power use |
| Temperature Stability | Keeps food at safer, more even temperatures |
| Quick Defrost | Shorter defrost cycles, less downtime |
| Lower Maintenance | Fewer electric parts to fail |
Cons of Hot Gas Fridge Defrost Heater
Hot gas defrost heaters also have some challenges. Not every fridge can use this system. Some users may find it harder to install or maintain.
- Complex System Design: Hot gas defrosting needs extra valves and piping. The setup can look complicated compared to electric systems. Technicians need special training to work on these fridges.
- Higher Upfront Cost: The first installation often costs more. Businesses must invest in better controls and extra parts.
- Not Ideal for Small Units: Most home fridges do not use hot gas defrosting. The system works best in large, commercial refrigerators.
- Possible Refrigerant Leaks: More pipes and valves mean more places where leaks can happen. Regular checks help prevent problems, but they add to maintenance time.
Tip: If someone wants a Fridge Defrost Heater for a small kitchen or home, electric models usually fit better. Hot gas systems shine in big, busy spaces.
Fridge Defrost Heater Comparison
Efficiency
Efficiency matters a lot when picking a defrost system. Electric heaters often waste more energy because they turn electricity straight into heat. This process does not use energy as well as other methods. Hot gas defrost heaters use the heat from the fridge’s own system, so they work smarter and save more energy.
Here’s a table that shows how different systems compare:
| Defrost Method | Defrosting Efficiency (%) | Power Consumption (kW) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Heating | Low (no exact % given) | N/A | Lower efficiency than hot-gas methods |
| Hot-Gas Bypass (DeConfig0) | 43.8 | N/A | Highest efficiency, no extra energy needed |
| Hot-Gas Bypass (DeConfig1) | 38.5 | 8.4 – 9.2 | High energy use due to compressor operation |
| Hot-Gas Bypass (DeConfig2) | 42.5 | 2.8 – 3.6 | Least energy needed with dedicated compressor |
| Hot-Gas Bypass (DeConfig3a) | 42.0 | 2.6 – 3.6 | Good for wide range compressors, moderate power use |
| Hot-Gas Bypass (DeConfig3b) | 39.7 | 6.7 – 6.9 | Good for narrow range compressors, higher power use |
Hot gas systems usually reach 38.5% to 43.8% efficiency. Electric heaters do not reach these numbers. The chart below shows how hot gas defrosting stands out:
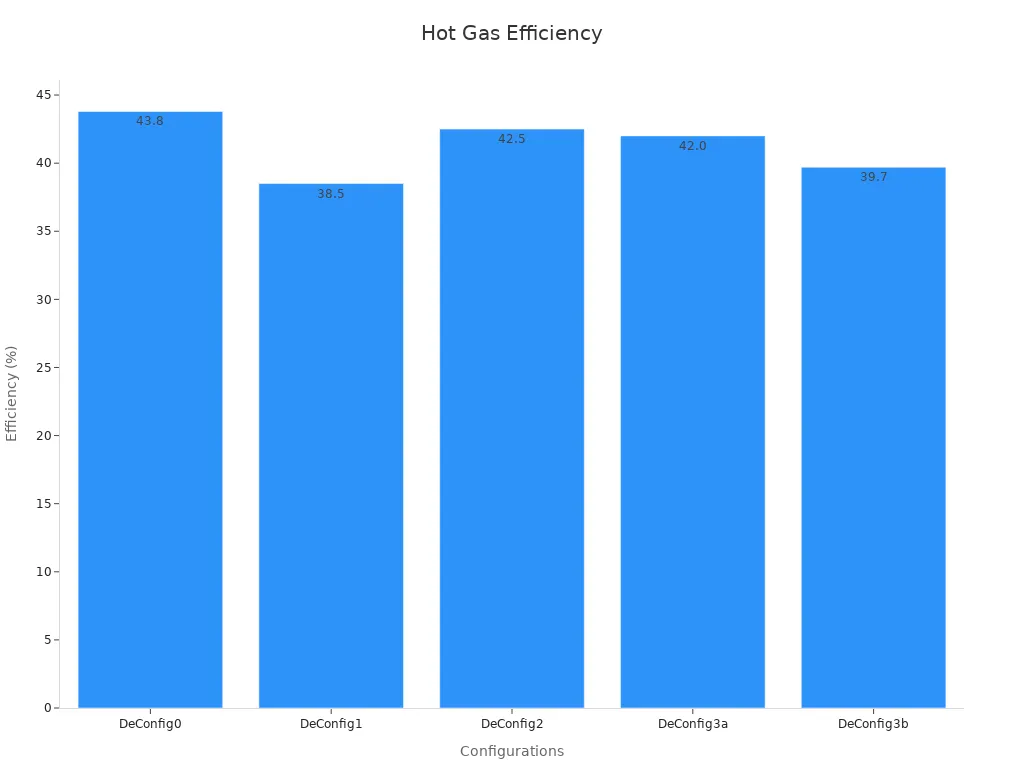
Tip: If someone wants to save energy, hot gas defrost heaters often work better than electric ones.
Cost
Cost can make a big difference for families and businesses. Electric defrost heaters usually cost less to buy and install. Most home fridges use this type because it is simple and affordable. Hot gas systems cost more at first. They need extra pipes and special controls, which can raise the price.
- Electric heaters: Lower upfront cost, easy to replace.
- Hot gas systems: Higher initial cost, but may save money over time by using less energy.
People who run large stores or restaurants often pick hot gas systems. They pay more at the start but save on energy bills later.
Maintenance
Maintenance keeps a Fridge Defrost Heater working well. Electric heaters need little care. Most users just clean the coils and check the controls now and then. If something breaks, parts are easy to find and fix.
Hot gas systems need more attention. They have more pipes and valves, so technicians must check for leaks and make sure everything works right. These systems may need a trained expert for repairs.
- Electric heaters: Simple upkeep, easy for most people.
- Hot gas systems: More complex, best for places with trained staff.
Note: Regular cleaning and check-ups help both systems last longer and work better.
Suitability for Different Environments
Choosing the right defrost heater depends on where it will be used. Electric and hot gas defrost heaters each have strengths that make them better suited for specific environments. Let’s explore how they perform in different settings.
Household Use
Electric defrost heaters are a common choice for home refrigerators. They’re simple, reliable, and cost-effective. Most households prefer them because they don’t require complex installations or maintenance. However, their energy efficiency is lower compared to hot gas systems. Studies show that electric heating defrosting achieves an efficiency of 30.3% to 48%, making it less environmentally friendly. Despite this, their affordability and ease of use make them ideal for small-scale applications.
Commercial and Industrial Settings
Hot gas defrost heaters excel in commercial environments like grocery stores, restaurants, and warehouses. These systems use waste heat from the refrigeration cycle, which boosts energy efficiency. With defrosting efficiencies reaching up to 50.84%, they outperform electric heaters in larger systems. Businesses benefit from lower energy costs and faster defrost cycles, which help maintain food quality. However, the initial setup can be more expensive due to the need for additional components like valves and piping.
Outdoor and Low-Temperature Applications
In outdoor or extremely cold environments, hot gas systems often require auxiliary heat to maintain efficiency. For instance, combining hot gas bypass with auxiliary heating can achieve up to 80% efficiency at 32°C ambient temperatures. This setup ensures reliable defrosting even in challenging conditions. Electric heaters, on the other hand, struggle in such settings due to heat loss and limited efficiency.
Here’s a quick comparison of defrosting methods and their suitability:
| Defrosting Method | Setting | Defrosting Efficiency (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Heating Defrosting | Household refrigerators | 30.3 – 48 | Affordable and simple, but less efficient and environmentally friendly. |
| Hot Gas Bypass Defrosting | Commercial refrigerators | Up to 50.84 | Energy-efficient, ideal for large systems, but higher upfront cost. |
| Hot Gas + Auxiliary Heating | Outdoor/low-temperature areas | Up to 80 | Reliable in extreme conditions, but requires additional power. |
Tip: For homes, electric heaters are practical and budget-friendly. For businesses or outdoor use, hot gas systems offer better efficiency and long-term savings.
Fridge Defrost Heater Recommendations
Best for Home Use
Most families want a fridge that works well and does not use too much energy. Electric defrost heaters fit this need. They are easy to install and simple to use. Many home refrigerators use a 200-watt heater. This power level keeps energy use low and melts frost in about 36 minutes. When engineers tested different heaters, they found that combining conductive and radiant heaters improved how evenly the freezer warmed up. Using a step-reduction power control strategy, the system cut energy use by 27%. The table below shows some important results from these tests:
| Metric | Result |
|---|---|
| Heater Power | 200 W |
| Energy Use per Cycle | 118.8 Wh |
| Defrost Duration | 36 minutes |
| Temperature Rise | 9.9 K |
| Energy Reduction (Optimized) | 27.1% |
Tip: Homeowners can save even more energy by choosing a fridge with smart controls that adjust the heater power during the defrost cycle.
Best for Commercial Settings
Large stores, restaurants, and warehouses need a system that can handle heavy use. Hot gas defrost heaters work best in these places. They use heat from the fridge’s own system, so they do not need extra electricity. This method keeps food at a steady temperature and melts frost quickly. Commercial fridges often run all day, so saving energy and keeping food safe is very important. Hot gas systems also need less maintenance because they have fewer electric parts.
- Hot gas defrosting works well for big spaces.
- It keeps food safe by holding a steady temperature.
- Businesses can save money on energy bills over time.
Best for Energy Savings
People who want to save the most energy should look at hot gas defrost systems. These systems use waste heat, so they do not add much to the power bill. In some cases, combining hot gas with extra heating can make the system even more efficient, especially in cold places. For homes, using an electric heater with smart controls can also help cut energy use. Choosing the right system depends on the size of the fridge and how often it runs.
Note: Always check if the fridge supports advanced control features or hot gas defrosting before buying.
Electric defrost heaters offer easy use and simple upkeep, making them great for homes. Hot gas systems save more energy and work best in busy commercial spaces. Studies show that smart heater controls and optimized designs can boost efficiency by up to 29.8% and cut energy use by 13%. For most families, electric heaters are the top pick. Businesses often choose hot gas for long-term savings.
Shengzhou Jinwei Electric Heating Appliance Co., Ltd. leads the world in heating element research, production, and sales. The company serves over 2,000 customers worldwide with top-quality products and trusted service.
FAQ
How often should someone run a fridge defrost heater?
Most fridges with automatic defrost run the heater every 8 to 24 hours. The system senses frost and starts the cycle. Users do not need to set a schedule.
Can a person install a hot gas defrost heater at home?
Hot gas defrost heaters work best in commercial fridges. Most home fridges do not support this system. A professional should handle any installation.
Do electric defrost heaters use a lot of electricity?
Electric defrost heaters use extra power during each cycle. Smart controls help lower energy use. Most families see only a small increase in their electricity bill.
What maintenance does a fridge defrost heater need?
Users should clean the coils and check the controls every few months. Electric heaters need little care. Hot gas systems may need a technician for regular checks.
Which defrost heater is safer for food storage?
Both types keep food safe when used correctly. Hot gas systems hold a steadier temperature, which helps protect food quality in busy kitchens.
Post time: Jun-14-2025




