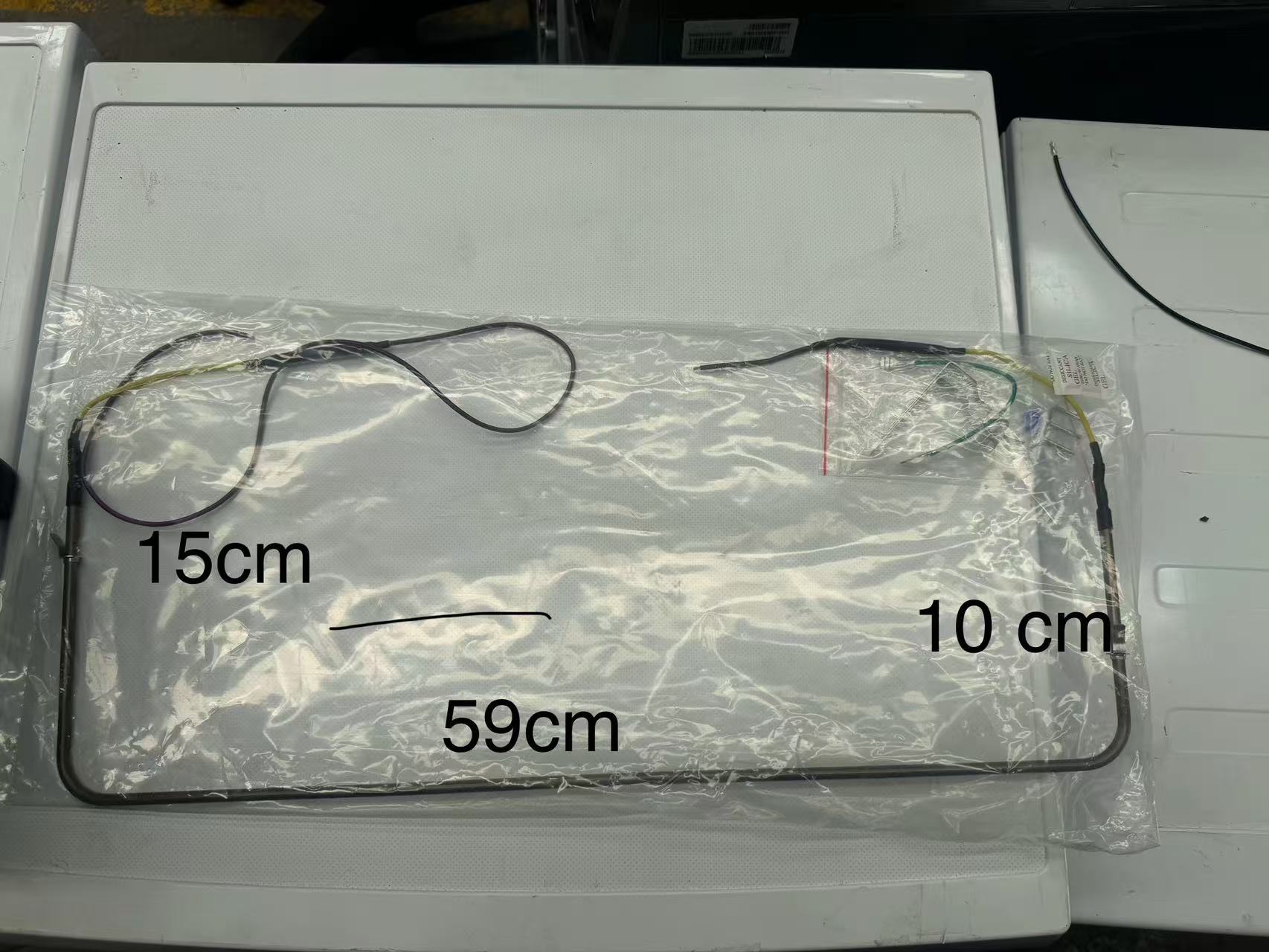
The defrost heater element is one of the indispensable core components in refrigerators and freezers. Its main responsibility is to prevent the formation of frost by melting the ice layer accumulated on the evaporator coils. The design of defrost heater tube is crucial for maintaining the normal operation of the equipment. Specifically, when the air inside the refrigerator or freezer passes through the evaporator for cooling, the moisture in the air may condense and gradually freeze on the surface of the evaporator. If these frost layers are not removed in time, they will gradually thicken and impede the effective circulation of cold air, thereby affecting the uniformity and stability of the internal temperature of the equipment.
To ensure that refrigerators or freezers can continuously provide a constant low-temperature environment, manufacturers usually install an automatic defrosting system in the equipment. The core component of this system is the defrost heating element, which starts at predetermined time intervals and transfers an appropriate amount of heat to the evaporator coils to melt the accumulated ice. This periodic defrosting operation not only helps maintain smooth air circulation inside the equipment but also significantly improves the refrigeration efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
The principle of defrosting in refrigerators – What is a wind-cooled refrigerator
The greatest advantage of a wind-cooled refrigerator is that it has no frost. Unlike refrigerators with refrigeration systems, a wind-cooled refrigerator does not have a constantly damp interior, and food does not stick together. Moreover, a wind-cooled refrigerator has a continuous circulation of cold air, which is filtered by the deodorization system, and the internal smell will be kept fresh for a long time, without the unpleasant “refrigerator smell” anymore. A wind-cooled refrigerator is not without frost; rather, the frost condenses on the evaporator. Since it is inside the refrigerator, we cannot directly see it with the refrigerator door open, so it is figuratively called frost-free. Additionally, because a wind-cooled refrigerator can automatically defrost.
The defrosting principle of a wind-cooled refrigerator – Working principle of defrosting in a wind-cooled refrigerator
After the defrosting process is completed in the previous cycle, the defrosting timer contacts the gray line and the orange line are connected, and the timer, compressor, and fan all start running simultaneously. The defrosting timer is connected in series with the defrost heater, but due to the larger internal resistance of the defrost timer and the smaller internal resistance of the defrost heater, most of the voltage is applied to the defrost timer, and the defrost heater generates very little heat. When the defrost timer and the compressor run simultaneously for a cumulative total of 8 hours, the contacts of the defrost timer’s gray line and orange line are connected. The defrost heater is directly powered by the fuse and the defrost switch, and the defrost motor is short-circuited by the defrost temperature control switch. The defrost timer stops running.
When the frost has completely melted, when the surface temperature of the evaporator rises to 10-16°C, the defrost temperature control switch contacts are disconnected from the defrost circuit, and at the same time, the defrost timer starts running. After about 5 minutes, the contacts of the gray line and the orange line are connected again, completing one automatic defrosting process. The compressor and fan start running again for refrigeration. Then, when the temperature of the evaporator drops to the reset temperature of the defrost temperature control switch, the temperature control switch is closed to connect the defrost heater, preparing for the next defrosting.
However, if the defrost heating element malfunctions, such as due to aging, burning out, or poor circuit connections, it may prevent the defrost cycle from functioning properly. As a result, frost on the evaporator can accumulate rapidly, blocking the air flow path and making it difficult for the equipment to maintain the set temperature range. This situation not only affects the preservation of food but also imposes additional stress on key components like the compressor, and may even lead to equipment damage. Therefore, when you notice a decline in the cooling performance of your refrigerator or freezer, abnormal frost accumulation inside, or a significant increase in energy consumption, you should immediately check the status of the defrost system.
If you suspect that the defrost heating element is faulty, it is recommended that you take the following steps as soon as possible: First, disconnect the power supply of the equipment to ensure safety; second, use a multimeter to test the resistance value of the heating element to determine if it is within the normal working range; finally, if it is confirmed that the component is damaged, you need to purchase a new part that matches the original model for replacement. By maintaining and replacing faulty components in a timely manner, you can effectively extend the service life of the refrigerator or freezer and ensure that it is always in the best operating condition.
Post time: Apr-26-2025